01/11/23
Bench Card
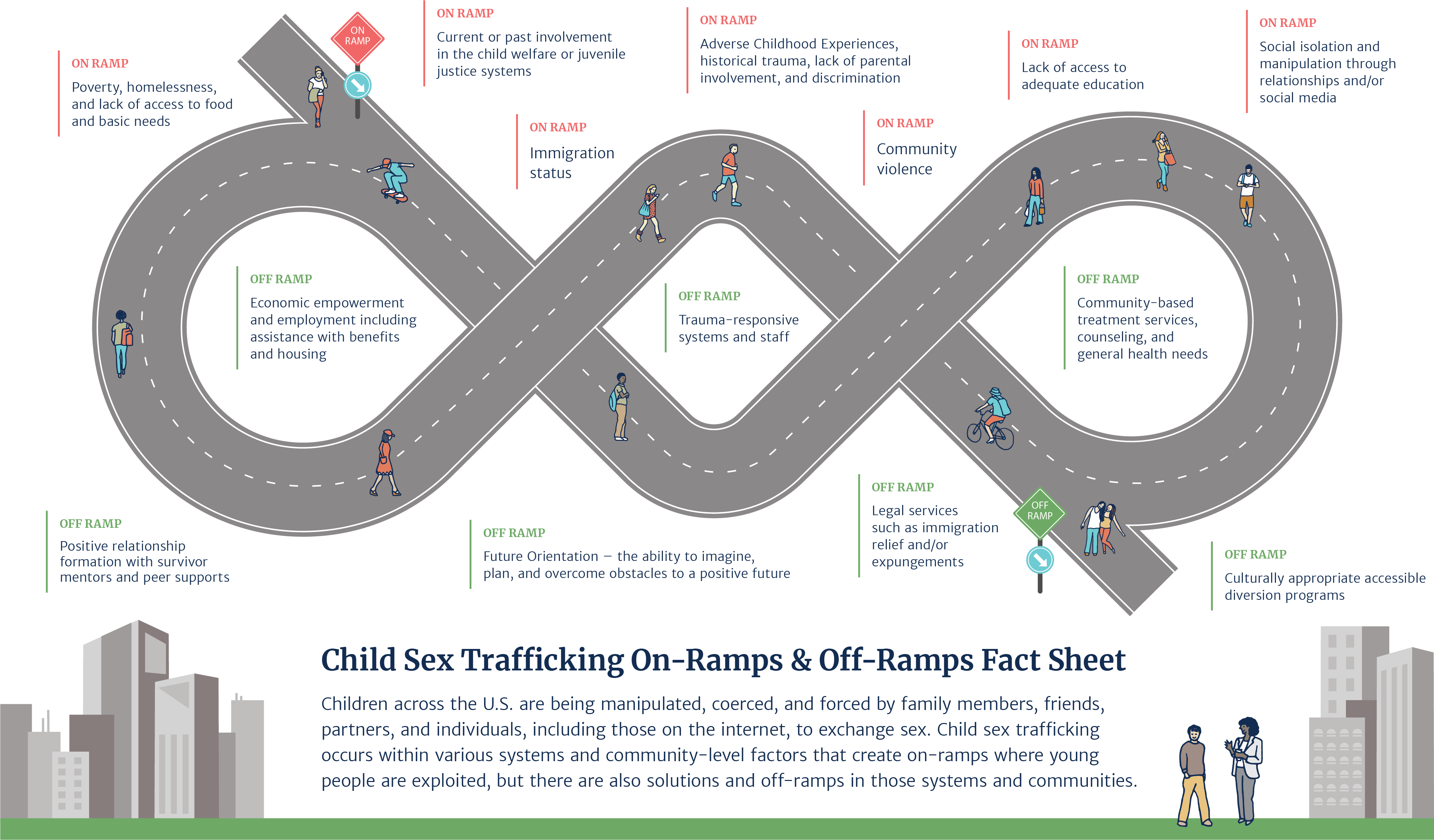
This infographic and fact sheet were developed in conversation with youth survivors and 39 stakeholders who provide training and/or technical assistance on child sexual exploitation and youth interventions across the country. These resources are intended to help courts and community stakeholders understand the common on-ramps into the life of trafficking and the most significant off-ramps for children who are being trafficked.